The Ultimate 2025 Guide to ISO/IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation for Indian Laboratories

In today’s competitive world, laboratories cannot survive on equipment and manpower alone — they need credibility. And when it comes to proving technical competence, there is one standard that stands above the rest: ISO/IEC 17025:2017.
This accreditation is not just a piece of paper. It is the difference between being seen as “just another lab” and being recognized as a globally competent, reliable, and trustworthy testing or calibration laboratory.
For Indian laboratories, ISO 17025 is even more important because industries like food, pharmaceuticals, environment, and construction rely heavily on accredited results. In fact, many regulatory bodies mandate ISO 17025 accreditation before accepting reports.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of ISO 17025, explaining its purpose, significance, the process of obtaining certification, and the best practices for maintaining it effectively.
What is ISO/IEC 17025:2017?
ISO/IEC 17025:2017 is an internationally recognized standard that lays down the requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. It covers:

- The technical competence of personnel and their ability to produce valid results
- The management system that ensures consistency and impartiality
- The processes and methods used in testing and calibration
In simpler terms, ISO 17025 ensures that a lab’s results are not just accurate once, but consistently accurate every single time.
ISO 9001 outlines broad quality management principles, whereas ISO 17025 focuses specifically on the standards required for laboratories involved in testing and calibration.
It ensures that labs are not just managed well, but also technically capable.
Why ISO 17025 Accreditation Matters for Indian Laboratories
Accreditation is not just about compliance; it directly affects business growth, trust, and global opportunities. Let’s explore the benefits:
1. Regulatory Compliance
In India, many regulatory bodies such as FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organization), and CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) require test results from ISO 17025-accredited labs. Without this, reports may not be legally accepted.
2. Increased Business Opportunities
In India, many regulatory bodies such as FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organization), and CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) require test results from ISO 17025-accredited labs. Without this, reports may not be legally accepted.
3. Enhanced Credibility and Customer Trust
In India, many regulatory bodies such as FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organization), and CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) require test results from ISO 17025-accredited labs. Without this, reports may not be legally accepted.
4. Global Recognition
In India, many regulatory bodies such as FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organization), and CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) require test results from ISO 17025-accredited labs. Without this, reports may not be legally accepted.
5. Operational Efficiency
In India, many regulatory bodies such as FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), CDSCO (Central Drugs Standard Control Organization), and CPCB (Central Pollution Control Board) require test results from ISO 17025-accredited labs. Without this, reports may not be legally accepted.
Key Clauses of ISO/IEC 17025:2017

The standard is divided into five main sections, each addressing a different area of laboratory functioning.
1. General Requirements
Impartiality:
The lab must avoid bias in its testing and calibration activities. For example, a food testing lab cannot show favorable results to a client just to retain business.Confidentiality:
Client data and results must remain secure and should not be disclosed without proper authorization.
2. Structural Requirements
The lab must be a legal entity or part of a legal entity.
Clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting structures must be defined. For instance, who is responsible for quality checks, who maintains calibration records, and who communicates with NABL.
3. Resource Requirements
Personnel:
Staff must be trained and competent in the methods they perform.Equipment:
It is essential that all instruments are regularly calibrated and well-maintained to ensure accuracy and reliability.Facilities:
The environmental factors, including temperature and humidity, must be controlled to ensure they do not influence the accuracy of results.Reference Standards:
Proper reference materials must be used to ensure accuracy.
4. Process Requirements
Validated Methods:
Every test method must be proven to produce accurate results.Measurement Uncertainty:
Labs must estimate and record the possible uncertainty in their results.Reporting:
Results must be presented clearly, including details like units, test methods, and measurement uncertainty.Handling Non-Conforming Work:
If results are questionable, the lab must stop, investigate, and take corrective action.
5. Management System Requirements
Labs must maintain documented policies, procedures, and records.
Internal audits must be conducted regularly to identify weaknesses.
Management reviews must be held to assess system performance and make improvements.
ISO 17025 Accreditation in India
In India, the National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL) is the authorized authority responsible for granting ISO 17025 accreditation.
Sectors where ISO 17025 is critical in India:
Pharmaceuticals:
Required for drug testing, stability studies, and calibration labs.Food & Beverages:
Mandatory for labs testing food safety under FSSAI.Environment:
NABL-accredited labs are needed for water, air, and soil analysis.Construction & Materials:
Building material and cement testing labs must be accredited for regulatory approvals.Automotive & Engineering:
Calibration labs ensure accuracy of instruments used in manufacturing.
Cities with Strong Demand:
Delhi NCR – Environmental and pharma testing labs
Mumbai & Pune – Automotive and food industry labs
Bangalore and Hyderabad – Key hubs for biotechnology, information technology, and electronics testing laboratories.
Chennai & Kolkata – Textile, industrial, and calibration labs
Step-by-Step Process to Achieve ISO 17025 Accreditation in India
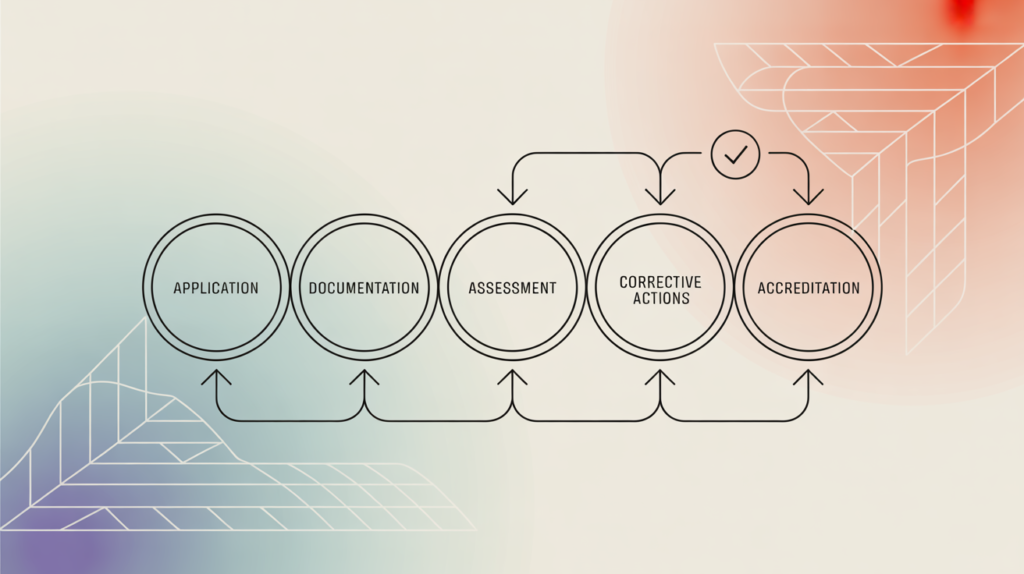
Getting accredited requires careful planning and systematic execution. Here’s a detailed roadmap:
Step 1: Gap Analysis
Before applying, labs must compare their current systems with ISO 17025 requirements. This identifies missing documentation, untrained staff, or equipment calibration gaps.
Step 2: Documentation
Prepare all required documents such as:
Quality Manual describing lab’s policies
SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures) for every activity
Equipment Calibration Records
Training Records of Staff
Step 3: Training and Awareness
Staff must be trained on ISO 17025 clauses. For example, a chemist should know not only how to perform a test but also how to document measurement uncertainty.
Step 4: Implementation
Start following the documented procedures. Maintain calibration schedules, record environmental conditions, and document all activities.
Step 5: Internal Audit
Conduct a mock audit before applying to NABL. This helps fix issues internally.
Step 6: Apply to NABL
Submit the required documents through the NABL portal and complete the payment of the applicable fees.
Step 7: Assessment
NABL will send assessors to evaluate your lab. They will review documents, staff competence, equipment records, and test results.
Step 8: Corrective Actions
If assessors find non-conformities, you must submit corrective action reports with evidence.
Step 9: Accreditation
Once all non-conformities are closed, NABL grants accreditation.
Common Challenges Indian Labs Face
- Poor Documentation: Many labs have good practices but fail to document them.
- Equipment Calibration Issues: Instruments are used without proper calibration certificates.
- Staff Competence: Staff may lack training on ISO 17025 requirements.
- Audit Stress: Labs often fail audits due to lack of internal mock assessments.
- Delayed Corrective Actions: Non-conformities take too long to be resolved.
Myths vs Facts
❌ Myth: ISO 17025 applies only to large laboratories
✅ Fact: Small laboratories can also achieve certification and leverage it to attract more clients.❌ Myth: Accreditation is permanent
✅ Fact: It requires periodic surveillance and renewal audits.❌ Myth: ISO 17025 is only about paperwork
✅ Fact: It is equally about technical accuracy and staff competence.
Audit Preparation Checklist
✔️ Calibration records updated and traceable
✔️ Training records available for all staff
✔️ SOPs documented and followed consistently
✔️ Measurement uncertainty calculated and recorded
✔️ Internal audits completed with corrective actions documented
FAQs
Q1. What is ISO 17025 in simple words?
It is a globally recognized standard that guarantees testing and calibration laboratories possess the technical competence to consistently deliver accurate and reliable results..
Q2. Who provides ISO 17025 accreditation in India?
In India, NABL (under QCI) is the official accreditation body.
Q3. How long is ISO 17025 valid?
Accreditation is typically granted for a period of two years, during which surveillance audits are conducted to ensure ongoing compliance.
Q4. Can a lab lose its ISO 17025 accreditation?
Yes. If non-conformities are not addressed, or if the lab fails to meet surveillance audits, accreditation can be suspended or withdrawn.
Q5. What is the cost of ISO 17025 accreditation in India?
Costs vary depending on lab size, scope, and consultancy support, typically ranging from ₹3 lakhs to ₹10 lakhs.
Q6. Is ISO 17025 mandatory for food labs in India?
Yes. Under FSSAI, only ISO 17025-accredited labs are recognized for official food testing.
Q7. Can calibration labs operate without ISO 17025?
They can operate, but their calibration certificates may not be accepted by many clients, especially in regulated industries.
Q8. How to train staff for ISO 17025?
Through structured training programs, workshops, and internal awareness sessions focused on both documentation and technical competence.
Q9. What documents are required for NABL application?
Quality manual, standard operating procedures (SOPs), calibration logs, training documentation, audit findings, and management review reports.
Q10. How often are surveillance audits done?
Typically once a year, to ensure continued compliance.
Q11. What is measurement uncertainty?
It is the range of doubt in test results, which must be calculated and reported by labs.
Q12. Can ISO 9001 labs easily upgrade to ISO 17025?
Yes, because ISO 9001 already has a quality system. However, ISO 17025 requires additional technical competence.
Q13. What happens if non-conformities are not closed?
Accreditation can be delayed, suspended, or cancelled.
Q14. How is ISO 17025 different from ISO 15189?
ISO 17025 is for testing and calibration labs, while ISO 15189 is for medical laboratories.
Q15. Does ISO 17025 apply to R&D labs?
Yes, if the lab provides test or calibration results used in research or product development.
Q16. Can international clients accept Indian ISO 17025 reports?
Yes, this is possible due to NABL’s recognition under ILAC and APAC Mutual Recognition Arrangements (MRA).
Q17. What is the role of proficiency testing?
It ensures labs can consistently produce accurate results by comparing with other labs.
Q18. How do labs maintain impartiality?
By creating policies that prevent conflicts of interest and ensuring staff are independent in decision-making.
Q19. Is remote (online) assessment possible in India?
Yes, NABL introduced remote assessments during COVID-19 and continues to use them in certain cases.
Q20. What are the renewal requirements?
Labs must undergo a re-assessment every two years and maintain compliance in the interim.

